Annotation
- Introduction
- Fundamentals of Contract Testing
- Implementing Contract Testing with Pact Framework
- AI-Enhanced Contract Testing
- Pricing and Tool Selection
- Core Framework Features
- Practical Applications
- Pros and Cons
- Conclusion
AI-Powered Contract Testing Guide: Pact Framework & Best Practices
Explore how AI-powered contract testing with Pact framework automates service verification, reduces integration issues, and accelerates microservices

Introduction
Contract testing revolutionizes how development teams verify service interactions in distributed systems. This methodology enables independent testing of consumer and provider services, eliminating complex integration environments. When combined with AI generation, contract testing becomes even more powerful, automating test creation and accelerating development cycles. This comprehensive guide explores how AI-enhanced contract testing works, its implementation with the Pact framework, and practical strategies for modern development teams.
Fundamentals of Contract Testing
What is Contract Testing?
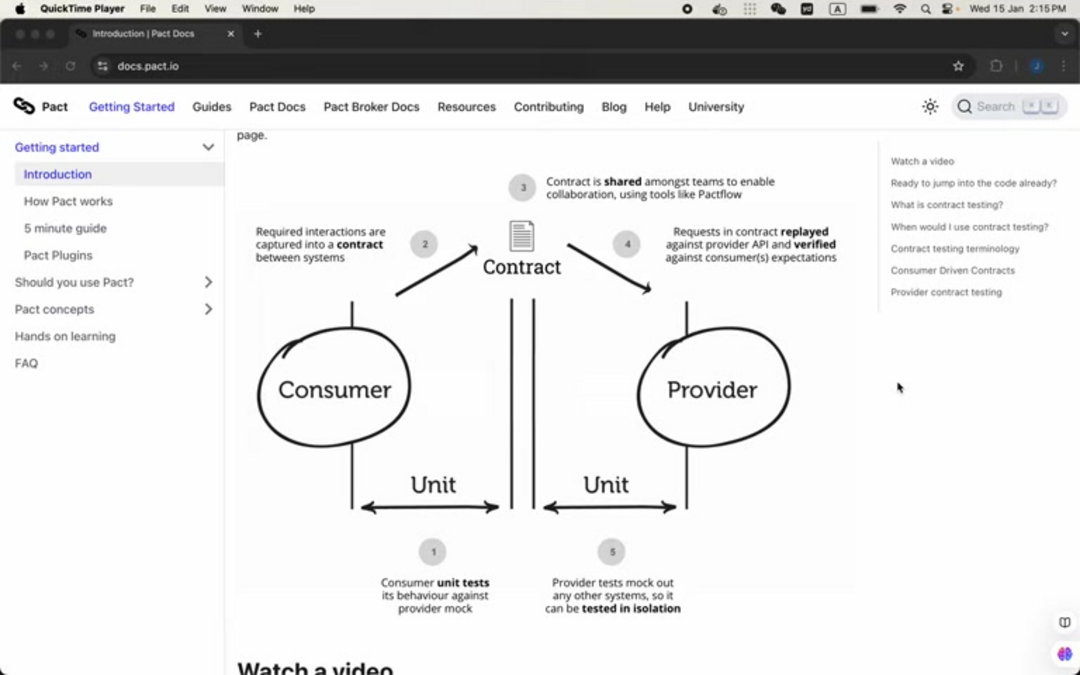
Contract testing represents a paradigm shift in software verification methodology. Unlike traditional integration testing that requires all dependent services to be running simultaneously, contract testing focuses on defining and validating the agreements between service consumers and providers. This approach captures expected interactions in a formal contract that both parties must honor, enabling teams to test services in isolation while ensuring compatibility across the entire system.
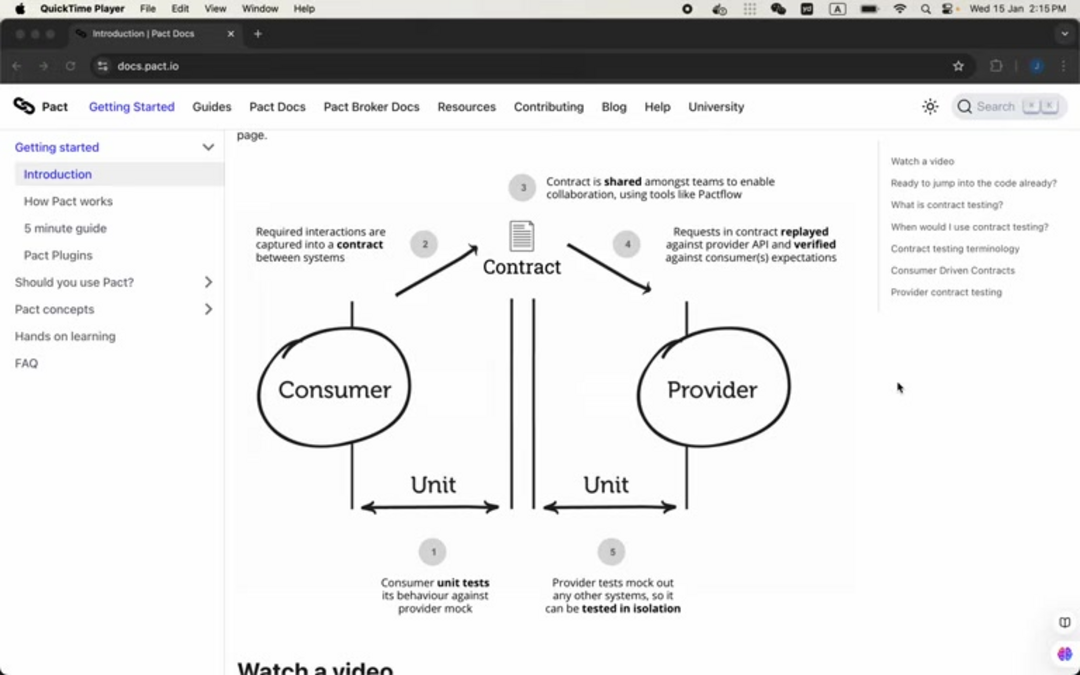
The core concept revolves around consumer-driven contracts, where the service consumer defines its expectations of the provider's API behavior. These expectations include request formats, response structures, status codes, and data schemas. The provider then verifies that its implementation satisfies these contracts, creating a reliable feedback loop that prevents integration failures before they reach production environments. This methodology is particularly valuable in CI/CD tool pipelines where rapid feedback is essential.
Key benefits of adopting contract testing include:
- Reduced testing dependencies: Services can be validated independently without complex environment setups
- Accelerated feedback cycles: Issues surface during development rather than integration phases
- Enhanced team collaboration: Clear contract definitions facilitate communication between distributed teams
- Improved system reliability: Consistent verification prevents breaking changes in production
- Cost efficiency: Simplified testing infrastructure reduces maintenance overhead
Contract Testing vs Traditional Integration Testing
Traditional integration testing approaches often create bottlenecks in modern development workflows. These methods typically require complete test environments with all dependent services running, which becomes increasingly complex in microservices architectures with dozens or hundreds of interconnected components. The setup time, maintenance overhead, and coordination challenges can significantly slow down development velocity.
Contract testing addresses these limitations by decoupling service verification. Instead of testing end-to-end workflows, it validates that each service adheres to its published contracts. This approach enables parallel development, faster test execution, and earlier detection of compatibility issues. Teams can integrate contract testing into their testing and QA processes without the overhead of maintaining complex integration environments.
Implementing Contract Testing with Pact Framework
Pact Framework Overview
Pact has emerged as the industry-leading open-source framework for implementing contract testing across diverse technology stacks. Supporting multiple programming languages including Java, JavaScript, Python, Ruby, and .NET, Pact provides a consistent approach to defining and verifying service contracts. The framework's workflow follows a structured process that ensures reliable contract validation throughout the development lifecycle.
The Pact workflow encompasses five critical stages:
- Consumer expectation definition: Development teams specify how their service expects to interact with provider APIs
- Contract generation: Pact automatically creates machine-readable contracts from consumer tests
- Provider verification: Provider services validate their implementation against generated contracts
- Contract publication: Verified contracts are published to a central Pact Broker repository
- Continuous validation: Both consumers and providers continuously verify contract compliance
This structured approach integrates seamlessly with modern development practices and automation platforms, providing teams with reliable contract management throughout the software delivery pipeline.
Practical Example: User Service Contract Testing
Consider a common scenario where a User Consumer service needs to retrieve user profile information from a User Provider service. The consumer expects specific response formats, field types, and error handling behavior. Using Pact, the consumer team writes tests that define these expectations, generating a contract that specifies exactly how the provider should respond to various request scenarios.
The provider team then downloads this contract and runs verification tests against their service implementation. Any discrepancies between the provider's actual behavior and the consumer's expectations are immediately identified, allowing teams to resolve compatibility issues before deployment. This approach is particularly effective when integrated with version control systems to track contract evolution over time.
AI-Enhanced Contract Testing
Setting Up Mock Servers for Testing
Effective contract testing requires reliable mock servers that simulate provider behavior during consumer testing. Docker-based mock server setups provide consistent testing environments that can be easily shared across development teams. Using docker-compose configurations, teams can quickly spin up mock servers that accurately represent provider APIs, enabling comprehensive consumer testing without dependency on actual provider deployments.
These mock servers capture detailed interaction logs, providing developers with visibility into exactly how their consumers interact with provider APIs. This detailed logging helps identify subtle compatibility issues that might otherwise go unnoticed until integration testing phases. The mock server approach integrates well with API client tools and debugging utilities.
AI-Generated Unit Test Automation
The integration of AI generation represents a significant advancement in contract testing efficiency. By leveraging large language models, teams can automate the creation of comprehensive unit tests for both consumer expectations and provider verifications. The AI analyzes existing test patterns, contract definitions, and code structures to generate additional test cases that cover edge conditions, error scenarios, and boundary cases that human developers might overlook.

This AI-assisted approach dramatically reduces the manual effort required for test creation while improving test coverage and reliability. Development teams can focus on defining business requirements while AI handles the repetitive aspects of test implementation. The generated tests integrate seamlessly with existing code linting and quality tools to maintain code standards.
Pricing and Tool Selection
Teams implementing contract testing have several options ranging from fully open-source to enterprise-grade hosted solutions. The open-source Pact framework provides a cost-effective starting point with no licensing fees, though teams must account for infrastructure costs for self-hosting Pact Broker instances and maintenance overhead for updates and security patches.
PactFlow offers managed contract testing solutions with subscription-based pricing tiers designed for organizations of different sizes. These hosted solutions reduce operational overhead and provide enterprise features like advanced analytics, team management, and compliance reporting. The choice between self-hosted and managed solutions depends on team size, budget constraints, and internal DevOps capabilities.
Core Framework Features
Modern contract testing frameworks provide comprehensive capabilities that streamline the entire contract lifecycle. Key features include sophisticated contract definition tools that support various API protocols and data formats, advanced mocking capabilities that accurately simulate provider behavior, and robust verification engines that thoroughly validate provider compliance.
Contract broker integration serves as a critical component, providing centralized storage, version management, and discovery services for contracts across the organization. Version control features track contract evolution, enabling teams to understand how API expectations change over time and ensuring backward compatibility. These capabilities make contract testing frameworks invaluable for organizations implementing debugging and troubleshooting processes in distributed systems.
Practical Applications
Contract testing delivers significant value across various development scenarios, particularly in microservices architectures where service independence and compatibility are paramount. Teams can validate interactions between dozens of microservices without the overhead of complex integration environments, enabling faster deployment cycles and more reliable releases.
API version management represents another critical use case, where contract testing ensures backward compatibility as APIs evolve. Third-party service integration benefits greatly from contract testing, providing assurance that external services meet internal expectations without requiring access to third-party testing environments. These applications demonstrate how contract testing addresses real-world challenges in modern software development.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Accelerates test creation through AI automation
- Reduces manual testing effort and human error
- Enhances test coverage with comprehensive scenarios
- Identifies integration issues early in development
- Improves system reliability and compatibility
- Facilitates parallel development across teams
- Simplifies complex microservices testing
Disadvantages
- AI-generated tests may contain inaccuracies
- Requires careful human review and validation
- Dependent on AI model quality and training data
- Adds complexity to CI/CD pipeline configuration
- Needs ongoing maintenance as contracts evolve
Conclusion
AI-powered contract testing represents the evolution of software verification methodologies for modern distributed systems. By combining the structured approach of contract testing with the automation capabilities of AI generation, development teams can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and reliability. The Pact framework provides a robust foundation for implementation, while AI augmentation accelerates test creation and enhances coverage. As organizations continue to adopt microservices and distributed architectures, contract testing with AI automation will become increasingly essential for maintaining system integrity and accelerating delivery velocity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a Contract Broker in contract testing?
A Contract Broker serves as a central repository for storing, sharing, and versioning contracts between services. It enables teams to discover available contracts, track changes, and ensure all services test against the latest versions, facilitating collaboration and reducing integration risks.
How does AI generation improve contract testing efficiency?
AI generation automates unit test creation for both consumer expectations and provider verifications. It analyzes existing patterns to generate comprehensive test cases covering edge conditions and error scenarios, reducing manual effort while improving test coverage and reliability.
Is contract testing suitable for monolithic applications?
While ideal for microservices, contract testing also benefits monolithic applications with clear component boundaries. It ensures internal service interactions remain consistent and helps prevent breaking changes during refactoring or component updates.
What are common challenges when adopting contract testing?
Teams often face challenges in defining clear contracts, setting up Contract Brokers, integrating with CI/CD pipelines, and ensuring alignment between consumer and provider teams. Success requires commitment to collaboration and understanding contract testing benefits.
How does contract testing fit into CI/CD pipelines?
Contract testing integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines by providing early feedback on service compatibility, preventing breaking changes from reaching production, and enabling faster, more reliable deployments.