Annotation
- Introduction
- The Evolution of Governance Systems
- Historical Foundations of State Power
- Contemporary Governance Challenges
- Internet-First Governance Principles
- AI Applications in Modern Governance
- Judicial System Transformation
- Regulatory System Enhancement
- Immigration System Modernization
- Pros and Cons
- Conclusion
AI and Blockchain: Transforming Government for Digital Era
AI and blockchain technologies are transforming governance by enhancing efficiency, transparency, and citizen participation through digital

Introduction
The traditional government model, built on 20th-century bureaucracy and paper-based systems, faces unprecedented challenges in our digital era. Artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies offer revolutionary pathways to create more efficient, transparent, and equitable governance structures. This transformation requires embracing internet-first principles that decentralize power and empower citizens through technological innovation.
The Evolution of Governance Systems
Historical Foundations of State Power
Understanding modern governance requires examining its origins. When human groups expanded beyond small communities – typically around 150 individuals, known as Dunbar's number – informal social structures became insufficient.
 The emergence of written laws, exemplified by The Code of Hammurabi, provided scalable frameworks for cooperation and conflict resolution. These legal systems created the foundation for economic stability and societal growth by establishing predictable rules and shared expectations.
The emergence of written laws, exemplified by The Code of Hammurabi, provided scalable frameworks for cooperation and conflict resolution. These legal systems created the foundation for economic stability and societal growth by establishing predictable rules and shared expectations.
Francis Fukuyama's comprehensive work "The Origins of Political Order" demonstrates how diverse societies developed distinct paths toward state formation. The Western governmental model represents a technological achievement that integrated disparate populations into cohesive political units. However, as explored in modern decentralized governance platforms, these traditional structures now face limitations in our interconnected world.
Contemporary Governance Challenges
Modern states struggle with bureaucratic inertia and declining public trust.
 The Delaware judiciary, once a global standard for corporate law, shows signs of instability. Regulatory bodies like the SEC face criticism for inconsistent enforcement, particularly regarding emerging technologies like cryptocurrency. Western immigration systems have shifted from open borders to restrictive policies, while legislative bodies suffer from declining public confidence.
The Delaware judiciary, once a global standard for corporate law, shows signs of instability. Regulatory bodies like the SEC face criticism for inconsistent enforcement, particularly regarding emerging technologies like cryptocurrency. Western immigration systems have shifted from open borders to restrictive policies, while legislative bodies suffer from declining public confidence.
These challenges highlight the need for governance models that leverage AI automation platforms and blockchain transparency. The internet has transformed nearly every aspect of modern life – from communication and commerce to social interaction – yet government structures remain largely unchanged from their industrial-era designs.
Internet-First Governance Principles
The digital transformation demands a fundamental rethinking of governance through internet-first principles. With billions of people conducting daily activities online, government services must evolve to match this reality. AI agents and assistants can revolutionize public service delivery, while blockchain technology ensures transparency and accountability.
The internet has already transformed multiple sectors that governments traditionally regulated:
- Digital Communication: Traditional mail services have been largely replaced by instant digital messaging
- Transportation Networks: Ride-sharing platforms transformed urban mobility and tax regulation
- Space Exploration: Private companies like SpaceX have taken leadership roles from government agencies
- Financial Systems: Cryptocurrencies and digital payments create new monetary ecosystems
- Legislative Processes: Citizens demand greater transparency and participation in lawmaking
- Equal Access: The internet provides universal access to information and services
AI Applications in Modern Governance
Judicial System Transformation
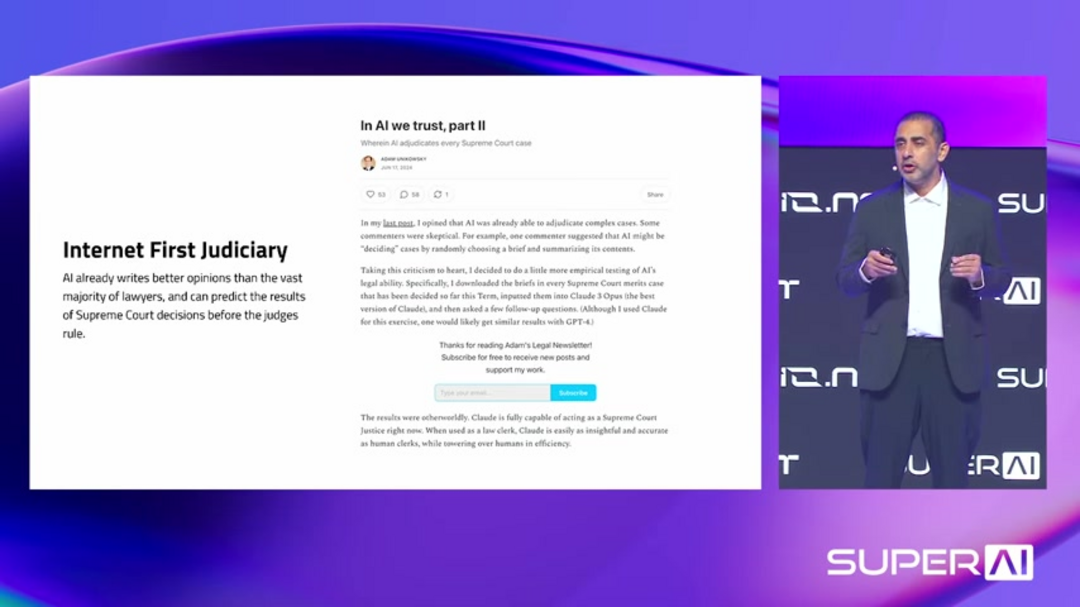
Artificial intelligence demonstrates remarkable potential in legal prediction and analysis. Research shows AI systems can forecast Supreme Court decisions with accuracy rivaling human experts.
 Integrating AI throughout the judicial system could provide citizens with reliable legal insights, reducing the need for expensive legal representation in straightforward cases.
Integrating AI throughout the judicial system could provide citizens with reliable legal insights, reducing the need for expensive legal representation in straightforward cases.
These systems offer data-driven legal interpretation that minimizes human bias while maintaining consistency across similar cases. Advanced AI chatbots could help citizens understand their legal rights and obligations, democratizing access to justice. The technology doesn't replace human judgment but enhances it with comprehensive data analysis and pattern recognition.
Regulatory System Enhancement
Regulatory bodies like the SEC could benefit significantly from AI integration. These systems can process thousands of regulatory actions simultaneously, identifying patterns and anomalies that human regulators might miss. AI can flag both compliance issues and exemplary behavior, creating a more nuanced regulatory environment.
The goal extends beyond punishment to improvement – AI systems can help organizations understand and correct compliance issues before they escalate. This approach creates what might be called "Internet First Equality," where regulations apply consistently and transparently across all market participants. Smart contract platforms could automate compliance verification, reducing administrative burdens while maintaining oversight.
Immigration System Modernization
AI applications in immigration could create fairer, more efficient border management. Machine learning systems can process complex eligibility criteria across thousands of applications, identifying patterns that indicate genuine need while flagging potential security concerns. These systems work at speeds impossible for human processors while maintaining consistent application of complex regulations.
Beyond simple approval/denial decisions, AI can provide insights for border policy improvements and identify systemic issues in immigration flows. This technology could help create immigration systems that balance security concerns with humanitarian values, potentially leading to better economic and social outcomes for both host countries and immigrants.

Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Significantly improved efficiency in public service delivery
- More consistent and data-driven decision-making processes
- Enhanced citizen participation through digital democracy tools
- Greater transparency in governmental operations and spending
- Reduced administrative costs through automation
- 24/7 accessibility to government services and information
- Personalized citizen services through AI analysis
Disadvantages
- Potential for algorithmic bias in automated decisions
- Job displacement in traditional bureaucratic roles
- Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in digital systems
- Privacy concerns with increased data collection
- Technical barriers for digitally excluded populations
Conclusion
The convergence of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology presents unprecedented opportunities to reinvent governance for the digital age. While traditional government structures served industrial societies effectively, they struggle to meet contemporary demands for efficiency, transparency, and citizen engagement. The transition toward internet-first governance requires careful implementation that addresses legitimate concerns about bias, privacy, and accessibility. However, the potential benefits – more responsive public services, reduced corruption, and greater citizen empowerment – make this technological transformation essential for building governments capable of meeting 21st-century challenges. The future of governance lies not in abandoning state structures but in augmenting them with technologies that enhance their effectiveness while preserving democratic values.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Network State concept?
The Network State proposes nation-building through online communities using technology to create new governance structures that transcend traditional geographic boundaries and empower digital citizens.
How can AI improve legal systems?
AI enhances legal systems through predictive analytics, consistent case evaluation, reduced bias, and improved access to legal information for citizens, though human oversight remains essential.
What are internet-first governance principles?
Internet-first governance prioritizes digital accessibility, real-time service delivery, transparent operations, and citizen participation through online platforms rather than traditional bureaucratic channels.
How does blockchain enhance government transparency?
Blockchain provides immutable records and smart contracts that ensure transparent, tamper-proof transactions and automated compliance, reducing corruption and increasing trust in public institutions.
What are the risks of AI in public services?
Risks include algorithmic bias, job displacement, cybersecurity threats, privacy issues, and digital exclusion, requiring robust oversight and inclusive design to mitigate negative impacts.