Annotation
- Introduction
- Unlocking Productivity: AI-Driven Coding Workflows
- The Power of AI in Software Development
- A Four-Step AI-Enhanced Coding Workflow
- Mastering the Art of Prompt Engineering for AI Code Generation
- Crafting Effective Prompts: Tips and Techniques
- Practical Strategies: Implementing AI in Your Projects
- Leveraging Cursor for AI-Assisted Coding
- Supabase Backend Integration Strategies
- Pricing Plans: Cursor, Claude, and More
- Tool Cost Analysis
- Pros and Cons
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
AI Coding Tools: Boost Development Efficiency with Cursor and AI Assistants
AI-powered coding assistants like Cursor and Claude transform development workflows by automating tasks, generating code, and boosting productivity.

Introduction
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally reshaping software development workflows, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance productivity and streamline coding processes. This comprehensive guide explores how AI-powered tools like Cursor, Claude, and GitHub Copilot can transform your development approach, providing practical strategies for implementation while addressing both the remarkable benefits and important limitations of AI-assisted coding.
Unlocking Productivity: AI-Driven Coding Workflows
The Power of AI in Software Development
The integration of artificial intelligence into software development represents a paradigm shift rather than incremental improvement. Modern AI coding assistants can automate repetitive tasks, generate boilerplate code, and identify potential errors before they become problematic. This automation allows developers to focus on higher-level architectural decisions and creative problem-solving rather than mundane implementation details.
Beyond simple automation, AI tools provide contextual understanding that adapts to individual coding styles and project requirements. This personalized assistance makes them particularly valuable for developers working across multiple IDE environments and programming languages. The technology has evolved from basic code completion to sophisticated pattern recognition and intelligent suggestion systems that learn from your coding habits.
A Four-Step AI-Enhanced Coding Workflow
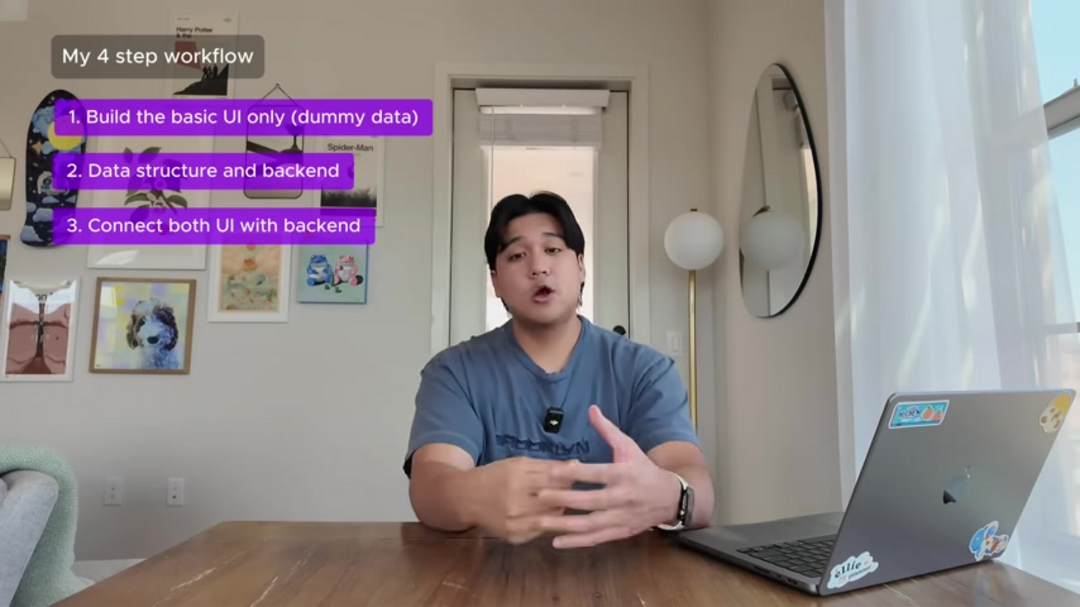
Implementing AI effectively requires a structured methodology that leverages the technology's strengths while maintaining development discipline. This proven four-step workflow provides a framework for integrating AI tools into your development process:
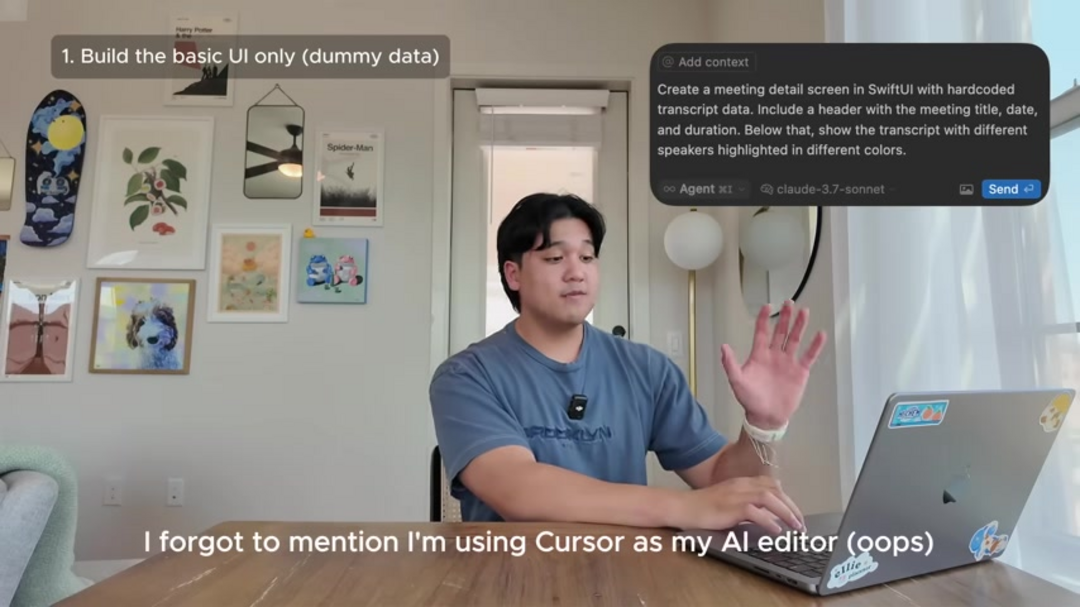
- Build the Basic UI with Dummy Data: Begin by creating the application interface using placeholder content. This approach allows for rapid visualization of user experience without backend complexity. Focus on layout, navigation, and user interaction patterns during this phase.
- Data Structure and Backend Development: With the UI framework established, direct AI tools to construct the necessary data models, API endpoints, and database schemas. This phase bridges visual design with functional architecture, ensuring the backend supports intended features.
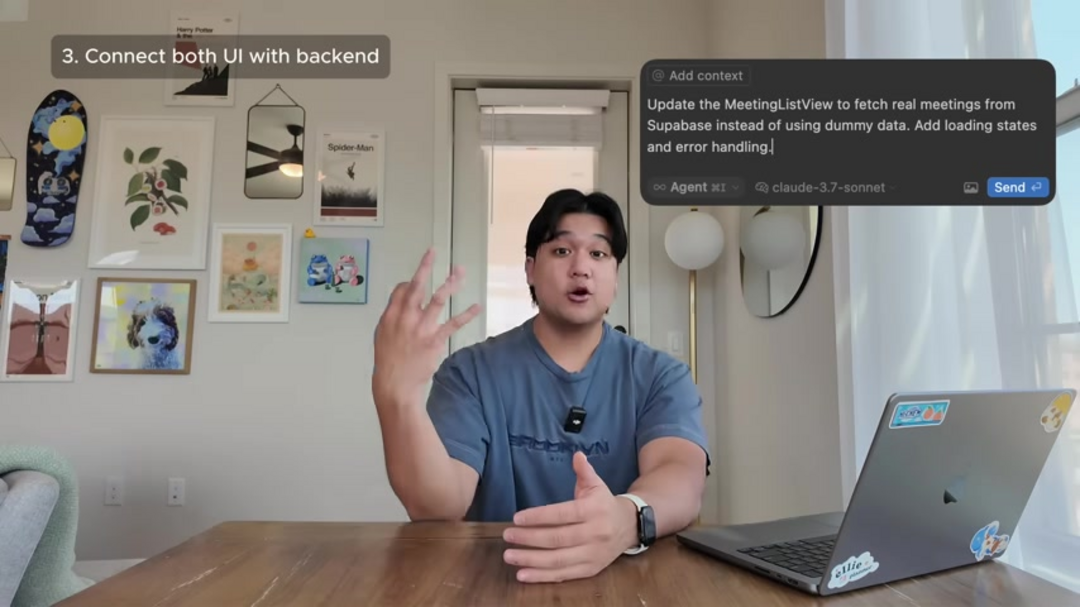
- Connect UI and Backend: Integrate frontend components with backend services, enabling dynamic data flow and user interactions. AI tools excel at automating this integration process, reducing manual configuration errors and ensuring consistent data handling.
- UI Polishing and Advanced Interactions: Finalize the user experience by adding animations, micro-interactions, and visual refinements. AI can suggest optimization techniques and identify areas where user experience can be enhanced through subtle improvements.
Mastering the Art of Prompt Engineering for AI Code Generation
Crafting Effective Prompts: Tips and Techniques
Prompt engineering represents the critical interface between developer intent and AI output quality. Well-crafted prompts significantly improve the relevance and accuracy of generated code. Consider these essential techniques for optimal results:
- Be Hyper-Specific: Provide detailed requirements including programming language, framework constraints, performance considerations, and integration points
- Provide Visual Context: Include screenshots, mockups, or detailed descriptions of UI elements to guide the AI's understanding of design requirements
- Iterate in Small Steps: Break complex tasks into manageable components, allowing for incremental refinement and error correction
- Establish Context Boundaries: Clearly define what the AI should reference from your codebase and what constitutes new functionality

Think of AI as a highly capable junior developer who requires clear, unambiguous instructions. The more specificity you provide in your prompts, the less time you'll spend correcting misunderstandings or inappropriate implementations.
Practical Strategies: Implementing AI in Your Projects
Leveraging Cursor for AI-Assisted Coding
Cursor stands out among AI assistants by providing deep integration with your development environment. Its agent mode analyzes your entire codebase to provide contextually relevant suggestions that align with your existing architecture and coding patterns. This contextual awareness distinguishes it from tools that operate in isolation.
The checkpoint functionality proves invaluable when experiments go awry. By maintaining version snapshots, developers can confidently explore alternative implementations knowing they can revert to stable states. This safety net encourages experimentation while protecting project integrity. The tool's ability to understand coding patterns across multiple files makes it particularly effective for refactoring and code optimization tasks.

Supabase Backend Integration Strategies
When working with Supabase, AI tools can dramatically accelerate backend development. Begin by requesting data models for your specific use cases – whether managing user sessions, application data, or complex relationships. The AI can then generate appropriate SQL commands and database configuration scripts.
Since tools like Cursor have access to your codebase context, they can extract existing patterns and preferences to ensure generated backend code aligns with your established conventions. This contextual awareness reduces integration friction and maintains code consistency across your project.
Pricing Plans: Cursor, Claude, and More
Tool Cost Analysis
Understanding the financial investment required for AI coding tools is essential for making informed decisions. Each platform offers distinct pricing structures and feature sets:
- GitHub Copilot: Provides subscription-based access to real-time code suggestions within popular IDEs. The service offers both monthly and annual billing options with consistent feature access across plans
- Claude: Operates on a tiered subscription model where higher pricing tiers provide access to more advanced models and increased usage limits. The latest models typically command premium pricing but deliver superior performance
- Cursor: Maintains a generous free tier with essential features, while the $20 monthly professional plan unlocks advanced capabilities including extended context windows and priority processing
When evaluating these tools, consider your project complexity, team size, and specific feature requirements. Many developers find that starting with free tiers provides sufficient functionality for initial experimentation before committing to paid plans.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Significantly accelerates coding speed through automation
- Improves code quality with intelligent error detection
- Enhances developer productivity across all project phases
- Provides creative solutions for complex programming challenges
- Automates repetitive tasks and boilerplate code generation
- Adapts to individual coding styles and preferences
- Offers real-time learning and improvement suggestions
Disadvantages
- May generate incorrect or hallucinated API references
- Can enter unproductive loops requiring manual intervention
- Variable code quality depending on prompt specificity
- Requires significant learning investment for optimal use
- Potential dependency development reducing fundamental skills
Conclusion
AI-powered coding tools represent a transformative development in software engineering, offering substantial productivity gains when implemented strategically. By mastering prompt engineering, adopting structured workflows, and maintaining appropriate oversight, developers can leverage these technologies to focus on creative problem-solving and architectural innovation. The future of software development lies in harmonious collaboration between human expertise and artificial intelligence, creating opportunities for more ambitious projects and accelerated innovation cycles across the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is coding knowledge necessary for using AI coding tools effectively?
While basic tasks can be accomplished with minimal programming experience, complex application development requires solid understanding of software principles. AI tools augment rather than replace developer expertise.
What are the primary limitations of AI in coding?
Key limitations include occasional API hallucination, potential looping behaviors, and variable output quality. Human oversight remains essential for validating AI-generated code.
Which AI model currently performs best for coding tasks?
Claude 3.7 demonstrates strong coding capabilities, though optimal choice depends on specific project requirements, programming languages, and integration needs.
How effective is AI at actual coding tasks?
AI demonstrates remarkable proficiency at generating functional code, identifying errors, and providing development suggestions. However, its effectiveness depends heavily on proper implementation and human guidance.
Is AI adoption increasing in software development?
AI integration in development workflows is experiencing rapid growth as tools mature and demonstrate tangible productivity benefits. Developers who embrace these technologies gain significant efficiency advantages.
Are we entering the era of 'vibe coding'?
While the concept of 'vibe coding' captures imagination, the reality remains nuanced. Developers provide essential direction and quality assurance while AI handles implementation details.