Annotation
- Introduction
- Summary of Image Recognition Applications
- Understanding Image Recognition Technology
- Applications Across Various Industries
- Practical Applications and Usage
- Core Technical Features
- Diverse Industry Applications
- Technical Implementation Process
- Current Limitations and Challenges
- Future Development Trends
- Pros and Cons
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Image Recognition Technology: AI Vision Transforming Industries | Complete Guide
Image recognition technology leverages AI to analyze and interpret visual data, driving innovations in retail, healthcare, security, and more through

Introduction
Image recognition technology represents one of the most transformative applications of artificial intelligence, enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information much like humans do. This sophisticated technology goes far beyond simple scanning to analyze complex visual patterns, identify objects, and even understand context within images. From retail and healthcare to security and automotive industries, image recognition is revolutionizing how machines interact with the visual world, creating new possibilities for automation, personalization, and efficiency across countless applications.
Summary of Image Recognition Applications
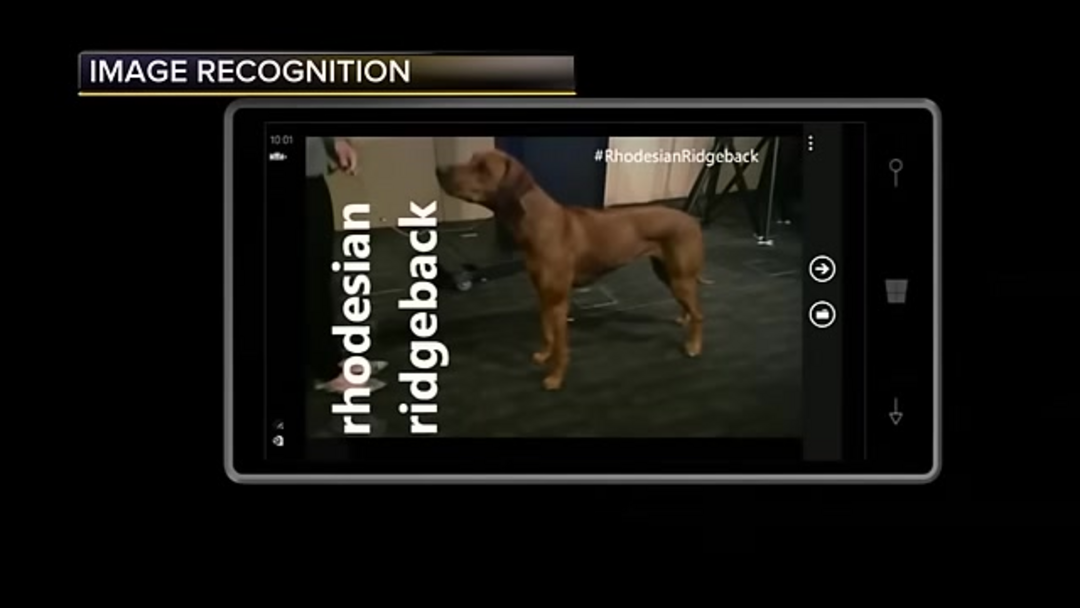
A visual overview of how image recognition technology is applied across various sectors, highlighting key use cases and benefits.
Understanding Image Recognition Technology
What is Image Recognition?
Image recognition constitutes a specialized branch of artificial intelligence that empowers computers and devices to identify and classify objects, people, locations, and activities within digital images and videos. Unlike conventional cameras that merely capture visual data, advanced image recognition systems employ complex algorithms to analyze and interpret visual content, enabling capabilities such as identifying specific dog breeds, authenticating identities, or recognizing artistic masterpieces.

The fundamental process involves sophisticated techniques like feature extraction, where the system identifies distinctive visual characteristics, and pattern matching, where these features are compared against extensive databases of known images. The effectiveness of any image recognition system depends critically on both the quality and volume of training data and the sophistication of its underlying algorithms. With continuous advancements in machine learning and deep learning architectures, modern image recognition has achieved unprecedented levels of accuracy and reliability across diverse applications.
It's crucial to distinguish image recognition from simpler technologies like barcode scanning or QR code reading. While barcodes and QR codes serve as encoded data shortcuts, genuine image recognition analyzes the actual visual content without requiring pre-encoded identifiers. This represents a significant leap forward in how devices perceive and interact with their environment.
Image Recognition vs. Facial Recognition
Although often confused, image recognition and facial recognition represent distinct technological domains with different applications and implications. Image recognition encompasses the broader field of identifying various objects, scenes, and visual elements within images. Facial recognition, conversely, constitutes a specialized subset focused specifically on identifying or verifying individuals based on unique facial biometric characteristics.

Facial recognition gained significant traction following major security events, where surveillance systems began identifying individuals at public venues by cross-referencing facial data against security databases. The fundamental distinction lies in their objectives: image recognition determines what something is, while facial recognition determines who someone is. This differentiation influences everything from technical implementation to ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks.
Core Attributes of Image Recognition Systems
Modern image recognition devices exhibit three essential characteristics that define their capabilities:
- Information Processing: These systems access massive databases containing millions of reference images, enabling them to match visual inputs against extensive knowledge repositories far exceeding human memory capacity.
- Discrimination Capability: Advanced systems excel at differentiating between visually similar objects, identifying subtle variations that human observers might miss, such as distinguishing between nearly identical product versions or detecting minute pattern differences.
- Automation Potential: Image recognition enables automated environmental analysis and spatial mapping, performing tasks that humans could accomplish manually but with significantly greater speed, consistency, and scalability while eliminating manual data entry requirements.
Applications Across Various Industries
Transforming Retail with Visual Search
Image recognition is fundamentally reshaping retail experiences through advanced visual search capabilities and product identification systems. Visual search technology allows consumers to locate products simply by capturing or uploading images, eliminating the limitations of traditional text-based searches that often struggle with describing complex or unfamiliar items accurately.

Industry leaders have pioneered these technologies, integrating image recognition into shopping applications that enable users to point their smartphone cameras at products and instantly access comprehensive information including pricing, availability, and customer reviews. This seamless integration significantly streamlines the purchasing journey while enhancing customer satisfaction.
Beyond consumer-facing applications, image recognition revolutionizes retail operations through improved inventory management and loss prevention. By analyzing security footage, retailers can identify shoplifting patterns and optimize store layouts to deter theft. These systems also provide real-time shelf monitoring, ensuring proper stock levels and improving supply chain logistics through automated inventory tracking.
Enhancing Security and Access Control
Facial recognition technology has become instrumental in modern security infrastructure and access control systems across multiple sectors. By analyzing unique facial characteristics, these systems provide secure identification and authorization mechanisms for restricted areas and sensitive facilities.
In transportation security, facial recognition accelerates passenger screening while identifying potential threats through database comparisons. Organizations employ facial verification for secure access to sensitive networks and facilities. The technology has also become ubiquitous in consumer devices, offering biometric authentication that's both more secure and convenient than traditional password systems.
Innovating Healthcare Diagnostics
Medical image recognition represents a breakthrough in healthcare diagnostics, enabling faster and more accurate analysis of medical imagery including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. These systems can identify subtle anomalies and patterns that might escape human detection, potentially leading to earlier disease identification and improved patient outcomes.
For instance, specialized algorithms can detect cancerous tumors in mammograms with remarkable accuracy, facilitating earlier breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. In pathology, image recognition assists in analyzing tissue samples and identifying disease markers, supporting pathologists in making precise diagnoses and developing personalized treatment strategies.
Practical Applications and Usage
Dog Breed Identification
Image recognition enables accurate dog breed identification through smartphone applications that analyze canine photographs. These apps examine distinctive features like eye shape, nose structure, and body proportions, comparing them against extensive breed databases to provide reliable identification. Applications demonstrate how this technology assists in animal welfare and pet ownership.

Enhanced Shopping Experiences
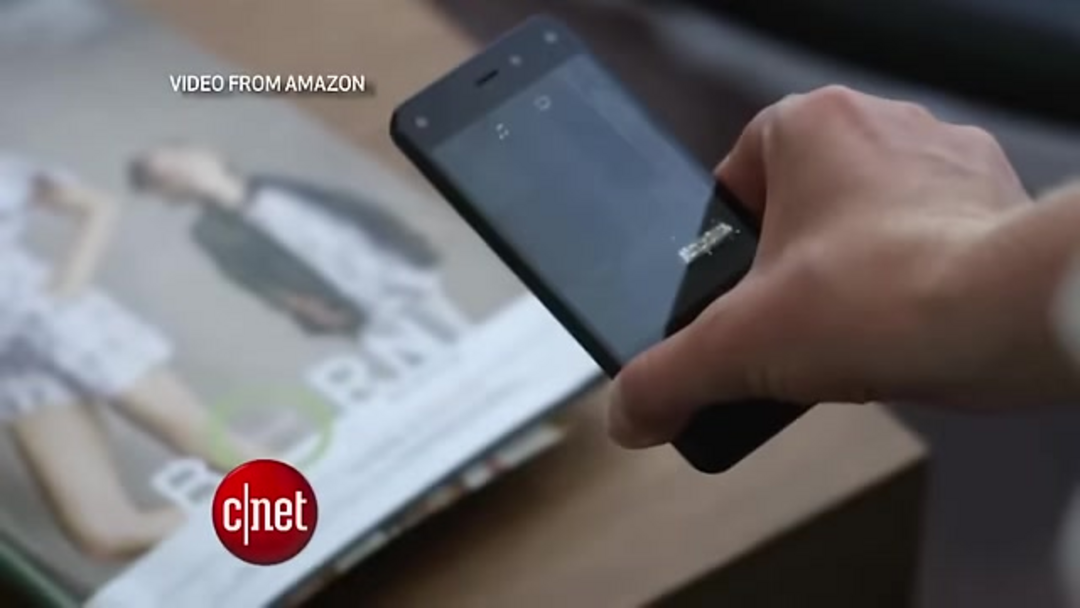
Image recognition transforms shopping through multiple innovative applications. Consumers can photograph furniture items and instantly find matching products with options to visualize different colors, access purchasing information, or discover similar styles. Package recognition enables users to photograph product packaging and immediately locate purchasing options, as demonstrated by dishwasher soap identification leading directly to online listings.

Cost Considerations and Solutions
Image recognition solution pricing varies significantly based on application complexity, database scale, and customization requirements. Cloud-based services typically employ pay-as-you-go models charging per image processed, offering cost-effective solutions for businesses with fluctuating needs.
For organizations requiring enhanced data security or greater control, on-premise solutions provide superior privacy protection though they demand substantial upfront hardware and software investments. Open-source alternatives offer cost-effective development frameworks but require significant technical expertise for implementation and maintenance.
Core Technical Features
Object Detection and Classification
A fundamental capability of image recognition systems involves detecting and classifying objects within visual content. This process identifies object locations and assigns them to predefined categories, enabling systems to recognize multiple elements in complex scenes like vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic signals in urban environments.
This functionality proves essential for applications including autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and robotic navigation, allowing devices to comprehend their surroundings and make informed decisions based on detected objects. The integration of AI automation platforms further enhances these capabilities through sophisticated workflow optimization.
Facial Recognition Capabilities
As previously discussed, facial recognition represents a specialized feature enabling identification or verification of individuals through facial biometric analysis. This involves extracting unique facial characteristics and comparing them against databases of known individuals.
This technology finds applications in security access control, identity verification, and social media functionality, providing convenient and secure user authentication while enabling personalized experiences. The development of advanced AI agents and assistants continues to expand these applications into new domains.
Scene Understanding and Analysis
Advanced image recognition systems extend beyond basic object detection to comprehend complete visual scenes and contexts. This involves analyzing relationships between objects and inferring broader image meaning, with some systems capable of generating automatic descriptive captions.
These capabilities benefit applications including visual search, content moderation, and accessibility tools for visually impaired users, enabling computers to understand image semantics and communicate this understanding through natural language. The evolution of AI model hosting services continues to make these advanced capabilities more accessible.
Diverse Industry Applications
Automotive Safety Systems
Image recognition plays a crucial role in advancing automotive safety through sophisticated driver monitoring systems. These systems employ cameras and recognition algorithms to monitor driver behavior, detecting indicators of fatigue, distraction, or impairment.

By analyzing eye movements, facial expressions, and head positioning, these systems identify declining alertness and can issue warnings, adjust vehicle settings, or assume control to prevent accidents. As these systems become standard in new vehicles, they promise significant reductions in accidents caused by human error.
Cultural and Artistic Applications
Image recognition creates new possibilities in cultural and artistic domains by enabling visual-based content discovery and information access. Museum visitors can photograph artworks and immediately access detailed information about artists, historical context, and artistic significance through their mobile devices.
This technology also facilitates music and content discovery through visual inputs, creating innovative pathways for cultural exploration and education. The integration with photo editing tools enhances these applications through improved image quality and analysis.
Augmented Reality Integration
Image recognition serves as a foundational technology for augmented reality applications by recognizing real-world objects and environments. AR apps overlay digital content onto physical spaces, creating immersive interactive experiences that blend virtual and real elements seamlessly.

Practical applications include virtual furniture placement in home environments, where apps recognize room dimensions and layout to accurately position virtual furniture models, allowing users to visualize products in their actual spaces before purchasing. These capabilities are increasingly supported by sophisticated AI APIs and SDKs that streamline development processes.
Technical Implementation Process
Image recognition systems employ a multi-stage analytical process to interpret visual content:
- Image Acquisition: The process begins with image capture using cameras or imaging devices, converting visual data into digital formats suitable for computational analysis.
- Image Preprocessing: Acquired images undergo enhancement procedures including noise reduction, contrast adjustment, and geometric correction to optimize analysis quality.
- Feature Extraction: Systems identify and extract relevant visual characteristics including edges, textures, color patterns, and distinctive landmarks that define objects and scenes.
- Pattern Matching: Extracted features undergo comparison against extensive databases using machine learning algorithms to identify closest matches and classifications.
- Classification and Interpretation: Based on matching results, systems classify images and interpret content, identifying specific objects, recognizing individuals, or understanding complete scenes.
This iterative process continuously refines through additional data and learning, progressively improving recognition accuracy and reliability across diverse applications. The availability of comprehensive image conversion tools further supports these processes through format optimization.
Current Limitations and Challenges
Despite significant advancements, image recognition technology still confronts several important limitations:
- Environmental Variability: Systems can struggle with recognition under different lighting conditions, viewing angles, or perspectives as these factors alter extracted features.
- Occlusion and Clutter: Partial object obscuration or complex backgrounds can interfere with feature extraction and accurate identification.
- Training Data Constraints: System accuracy depends heavily on training data quality and diversity, with limited datasets potentially failing to recognize underrepresented objects.
- Adversarial Vulnerabilities: Sophisticated attacks using subtly modified images can cause misclassification, posing security risks in critical applications.
- Computational Requirements: Advanced recognition systems often demand significant processing power and storage capacity.
Future Development Trends
Image recognition technology continues evolving with several promising development trajectories:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Ongoing machine learning research promises systems with improved accuracy, reliability, and robustness across diverse conditions.
- Industry Expansion: Technology adoption continues spreading into new sectors including agriculture, manufacturing, and education.
- AI Integration: Increasing integration with complementary AI technologies like natural language processing and robotics creates more intelligent autonomous systems.
- Edge Computing: Growing implementation of edge-based recognition reduces latency and enhances privacy through local processing.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing comprehensive ethical guidelines and regulatory standards ensures responsible technology deployment.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Significantly enhances operational efficiency across multiple industries
- Provides robust security through advanced access control systems
- Enables faster and more accurate medical diagnoses
- Creates innovative ways to interact with digital content
- Drives technological innovation across numerous sectors
- Automates repetitive visual analysis tasks effectively
- Improves customer experiences through personalized interactions
Disadvantages
- Involves substantial development and implementation costs
- Raises significant privacy concerns and potential misuse
- Accuracy can be compromised by environmental conditions
- Presents ongoing ethical challenges requiring careful regulation
- May exhibit bias based on training data limitations
Conclusion
Image recognition technology represents a transformative force across numerous industries, enabling machines to perceive and interpret visual information with increasing sophistication. From enhancing retail experiences and healthcare diagnostics to improving security systems and automotive safety, these technologies continue creating new possibilities for automation, personalization, and efficiency. As development progresses, we can anticipate even more accurate, reliable, and ethically implemented systems that further bridge the gap between human and machine visual understanding. The ongoing integration with complementary AI technologies promises to unlock unprecedented capabilities, fundamentally reshaping how we interact with technology and our visual environment across personal, commercial, and industrial contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How accurate is current image recognition technology?
Modern image recognition achieves over 99% accuracy in controlled environments like facial recognition, though performance varies with conditions. Factors affecting accuracy include lighting, image quality, training data diversity, and algorithm sophistication across different applications.
What's the difference between image recognition and computer vision?
Computer vision encompasses all aspects of how machines interpret visual data, while image recognition specifically focuses on identifying and classifying objects within images. Think of computer vision as the broader field and image recognition as one of its key applications.
Can image recognition work in real-time applications?
Yes, modern systems can process images in real-time for applications like autonomous vehicles, security monitoring, and augmented reality. Performance depends on hardware capabilities, algorithm efficiency, and network connectivity for cloud-based solutions.
What are the main ethical concerns with image recognition?
Key ethical issues include privacy violations through unauthorized surveillance, algorithmic bias based on training data, potential misuse for discrimination, and lack of transparency in decision-making processes requiring careful regulation and ethical frameworks.
How does image recognition benefit retail businesses?
Retail applications include visual search for product discovery, inventory management through shelf monitoring, theft prevention via security analysis, and personalized shopping experiences through customer behavior understanding and preference tracking.